What are proteoglycans?
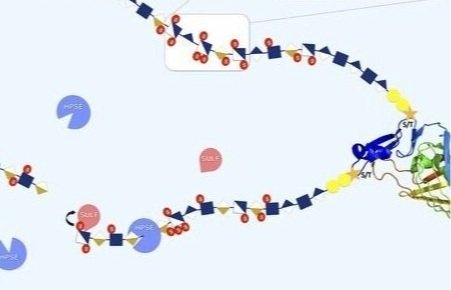
Almost half of proteins have one or more post-translational glycosylation modifications involving the addition of complex glycan structures. Proteoglycans are a class of glycosylated proteins with one or more glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains covalently attached to the core protein. The family encompasses a broad collection of glycoconjugates with a vast range of different biological functions served primarily by their core protein structures and diverse GAG chains interacting with multiple ligands. These biochemically distinct proteins play numerous roles in biology including development, cancer, ligands for infectious disease, Alzheimer’s, obesity, cardiovascular disease, kidney function and disease, as well as complement regulation, to name a few.